Hepatitis C: What You Need to Know
Infograph
Watch the video version of this information here.
Click here to download a PDF poster of this information.
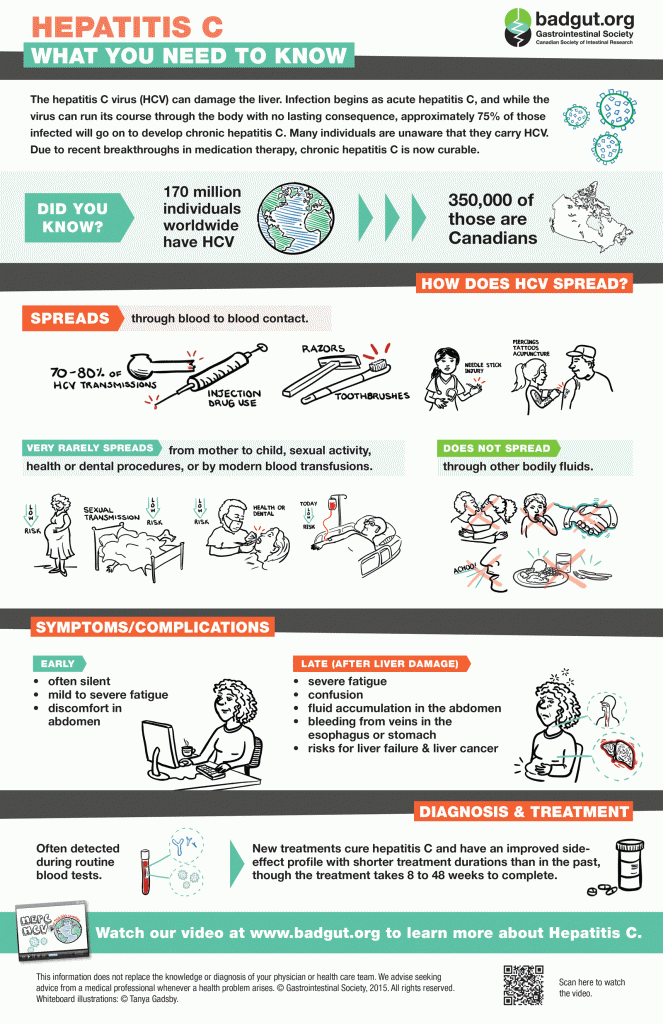 The hepatitis C virus (HCV) can damage the liver. Infection begins as acute hepatitis C, and while the virus can run its course through the body with no lasting consequence, approximately 75% of those infected will go on to develop chronic hepatitis C. Many individuals are unaware that they carry HCV. Due to recent breakthroughs in medication therapy, chronic hepatitis C is now curable.
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) can damage the liver. Infection begins as acute hepatitis C, and while the virus can run its course through the body with no lasting consequence, approximately 75% of those infected will go on to develop chronic hepatitis C. Many individuals are unaware that they carry HCV. Due to recent breakthroughs in medication therapy, chronic hepatitis C is now curable.
Did you know?
- 170 million individuals worldwide have HCV
- 350,000 of those are Canadians
How does HCV spread?
SPREADS
- through blood-to-blood contact.
VERY RARELY SPREADS
- from mother to child, sexual activity, health or dental procedures, or by modern blood transfusions.
DOES NOT SPREAD
- through other bodily fluids.
Symptoms/Complications
EARLY
- often silent
- mild to severe fatigue
- discomfort in abdomen
LATE (After Liver Damage)
- severe fatigue
- confusion
- fluid accumulation in the abdomen
- bleeding from veins in the esophagus or stomach
- risks for liver failure & liver cancer
Diagnosis & Treatment
- Often detected during routine blood tests.
- New treatments cure hepatitis C and have an improved side-effect profile with shorter treatment durations than in the past, though the treatment takes 8 to 48 weeks to complete.

